Mini Slide Show for #SWMMLive which reads I#nfoSWMM files in a @innovyze #ICM GUI pic.twitter.com/R6D7zVChQQ
— Robert E Dickinson (@RDickinson) June 25, 2014
Autodesk Technologist with Information about Stormwater Management Model (SWMM) for watershed water quality, hydrology and hydraulics modelers (Note this blog is not associated with the EPA). You will find Blog Posts on the Subjects of SWMM5, ICM SWMM, ICM InfoWorks, InfoSWMM and InfoSewer.
Wednesday, June 25, 2014
#SWMMLive which reads I#nfoSWMM files in a @innovyze #ICM GUI
Sunday, June 22, 2014
Peaking flow in InfoSewer Steady State applied as Total Flow in an EPS Simulation
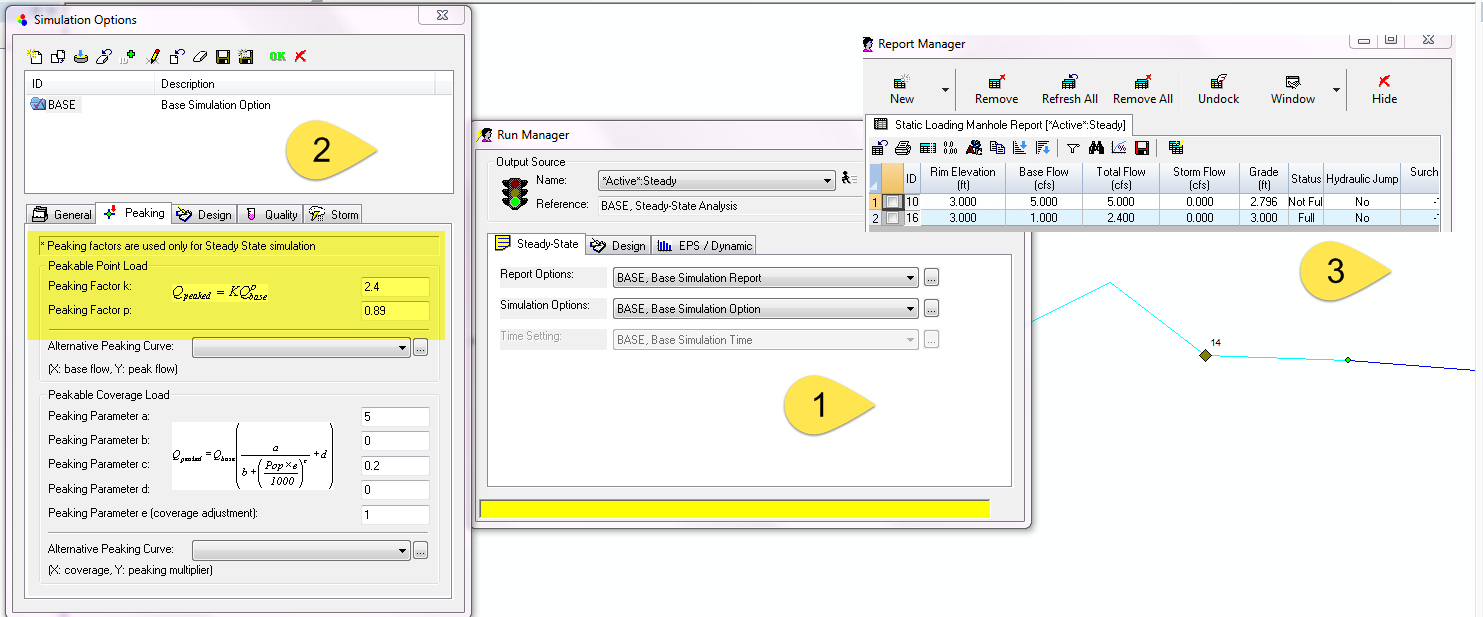
One of the advantages of the three Run options in InfoSewer (Bullet 1 in the image) which are Steady Sate, Design and Extended Period or EPS Modeling is that you can use Peaking Flow Factors for the Steady State Loading Manholes (Bullet 2 in the image). Unfortunately, you cannot use Peaking Factors for EPS simulations which is often a modeling issue. However, you can copy the Total Flow for each node in the Steady State Output Report and use this Total Flow as an EPS "other" loading (Bullet 3 in the image). In an EPS Simulation you can use the Advanced Force Main Modeling option and automatically have flow splits for Force Mains and model more complicated Force Main configurations. If you just simulate the EPS for one hour then you have a quasi steady state simulation with Total Flow (Unpeakable + Peakable) and the Advanced Force Main Solution.
A list of steps you need to take to use the Peak Flow from a Steady State Run in an EPS Simulation include
1. Use Peaking Factor in InfoSewer for Steady State
2. Copy Total Loads at Manholes
3. Use the Total Loads in an EPS simulation
4. Run the EPS Simulation for a short period of time
5. If might help to have two scenarios for this copy and pasting
6. Use the Advanced FM solution for only the EPS Simulation
2. Copy Total Loads at Manholes
3. Use the Total Loads in an EPS simulation
4. Run the EPS Simulation for a short period of time
5. If might help to have two scenarios for this copy and pasting
6. Use the Advanced FM solution for only the EPS Simulation
 |
| Peaking flow in InfoSewer Steady State applied as Total Flow in an EPS Simulation |
Wednesday, June 11, 2014
How to make a smaller model out of your larger InfoSWMM or H2OMap SWMM network
How to make a smaller model out of your larger InfoSWMM or H2OMap SWMM network:
- Make a domain and then an active facility from the domain for your larger network
- Export the Active Newtork in the current scenario to SWMM 5
- Import the smaller model from SWMM 5 into a different InfoSWMM model
- You now have a smaller model in InfoSWMM or H2OMap SWMM.
 |
| Steps to Make a Smaller Model from an InfoSWMM or H2OMap SWMM Model |
Sunday, June 8, 2014
d/D, q/Q for a Link in SWMM 5, InfoSWMM and H2oMap SWMM
d/D, q/Q for a Link in SWMM 5, InfoSWMM and H2oMap SWMM
How do we look at the various measures of "fullness" in a pipe of link in SWMM 5? Here we look at some graphs from InfoSWMM.
d/D is the pipe depth over the full depth of the link
q/Q is the current link flow over Qfull for the link (Q full is the full flow of a link based on Manning's equation) This Qfull is based on the bed slope of the link. You can have a q/Q or q/Qfull greater than 1 if the water surface slope is greater than the bed slope of a link. This is especially true for flat links where SWMM 5 has a minimum slope of 0.001
The image shown below shoes that at the peak flow in the links is greater than 1 even though the pipe is not full (d/D less than 1) for this model of flat slopes. Qfull is a comparison metric and not the result of the simulation.
How do we look at the various measures of "fullness" in a pipe of link in SWMM 5? Here we look at some graphs from InfoSWMM.
d/D is the pipe depth over the full depth of the link
q/Q is the current link flow over Qfull for the link (Q full is the full flow of a link based on Manning's equation) This Qfull is based on the bed slope of the link. You can have a q/Q or q/Qfull greater than 1 if the water surface slope is greater than the bed slope of a link. This is especially true for flat links where SWMM 5 has a minimum slope of 0.001
The image shown below shoes that at the peak flow in the links is greater than 1 even though the pipe is not full (d/D less than 1) for this model of flat slopes. Qfull is a comparison metric and not the result of the simulation.
 |
| d/D, q/Q for a Link in SWMM 5, InfoSWMM and H2oMap SWMM |
Friday, June 6, 2014
Urban frogs adapting to Urban Stormwater Networks in Taiwan
Urban frogs adapting to Urban Stormwater Networks in Taiwan
"The frogs have learned to overcome that limitation by calling from within storm drains, since the drains enhance both volume and duration, allowing the frogs' calls to reach receivers both nearby and farther away.
"Concrete drains are miniature canyons, but are not analogous to anything in Mientien tree frog natural habitats," the researchers say. "Therefore, it is interesting to find those frogs preferentially calling in the drains." The frogs have taken the human built environment and turned it into a tool, rather than an obstacle to overcome, allowing their species to survive an environment dominated by our species."
Wednesday, June 4, 2014
Cool Inlets, Suds, LID Images from Twitter
Come across some different takes on sensitive SuDS inlets and outlets... pic.twitter.com/ly8ruIjU8G
— susdrain @ CIRIA (@Sudsulike) May 17, 2014
KC approach to storm water management. pic.twitter.com/gS1eR9f2ek
— steve sinclair (@stevesinclair52) May 21, 2014
And another one, for all those thinking of retrofitting a rain garden or two... pic.twitter.com/KO6kyPD8H7
— susdrain @ CIRIA (@Sudsulike) May 17, 2014
RT @SuDSWales: Bioretention planter in Llanelli. Part of the @DwrCymru RainScape programme (soon to be on @sudsulike) pic.twitter.com/hPR3wuzX9e
— susdrain @ CIRIA (@Sudsulike) May 15, 2014
KC approach to storm water management. pic.twitter.com/gS1eR9f2ek
— steve sinclair (@stevesinclair52) May 21, 2014
Monday, June 2, 2014
New SWMM 5.1.006 is now available from the EPA Site
New SWMM 5.1.006 is now available from the EPA Site
http://www.epa.gov/nrmrl/wswrd/wq/models/swmm/
with these engine changes
http://www.epa.gov/nrmrl/wswrd/wq/models/swmm/
with these engine changes
-------------------------
Build 5.1.006 (5/19/2014)
-------------------------
Engine Updates:
1. The updating of the next time that detailed LID results
should be written to file during a simulation was modified
to avoid an off-by-one error.
2. The number of decimal places for hourly evaporation written
to a detailed LID report was increased.
3. The amount of soil water available for evaporation in
LID units with soil layers wasn't being limited by the
water remaining below the wilting point.
4. The equation that computes the rate of water infiltrating
into permeable pavement LIDs had a misplaced parenthesis.
5. There was a units conversion error in computing the
contribution of a pollutant in direct precipitation
to the water quality on a subcatchment.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
InfoSWMM: A 2030 AI-Assisted Study Guide
InfoSWMM: A 2030 AI-Assisted Study Guide delete InfoSWMM: A 2030 AI-Assisted Study Guide A comprehensive study guide for someone in 2030...
-
@Innovyze User forum where you can ask questions about our Water and Wastewater Products http://t.co/dwgCOo3fSP pic.twitter.com/R0QKG2dv...
-
Soffit Level ( pipe technology ) The top point of the inside open section of a pipe or box conduit. The soffit is the ...
-
Engine Error Number Description ERROR 101: memory allocation error. ...




